Benefits of Data Warehousing
Data warehouses offer a range of advantages that can transform how businesses function and make data-driven decisions. Here's a closer look at some of the key benefits:
Improved Data Quality and Consistency: One major challenge in organizations is dealing with data silos and inconsistencies across various departments. Data warehouses consolidate information from multiple sources into a central repository, ensuring a consistent format and structure. This facilitates data cleaning and transformation processes, resulting in trustworthy and reliable data for analysis.
Unified View of Business Operations: By bringing data together, data warehouses provide a holistic view of an organization's activities. This empowers businesses to analyze trends, identify correlations, and gain a deeper understanding of customer behavior, marketing effectiveness, operational bottlenecks, and more.
Enhanced Decision-Making: With access to high-quality, consistent data, businesses can make informed decisions backed by insights. Data warehouses enable robust reporting and analytics, allowing users to slice and dice data from various perspectives. This empowers data-driven decision making across all levels of the organization.
Historical Analysis and Trend Identification: Data warehouses are designed to store vast amounts of historical data. This enables businesses to track trends over time, identify seasonal patterns, and forecast future performance. This historical perspective is crucial for strategic planning and proactive business management.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Data warehouses eliminate the need to access and combine data from disparate sources. This saves significant time and effort for analysts and business users, allowing them to focus on extracting insights and value from the data.
Improved Data Security: Data security is a critical concern in today's data-driven world. Data warehouses offer centralized security measures, making it easier to control access, implement user permissions, and enforce data governance policies. This ensures that sensitive information is protected.
Potential for Automation: Data warehouses can be integrated with business intelligence (BI) tools and automation platforms. This allows businesses to automate tasks such as data extraction, transformation, and reporting. This frees up IT resources and reduces manual errors.
Scalability and Flexibility: Data warehouses are built to scale and accommodate
growing data volumes. As a business expands, the data warehouse can be easily
scaled to handle the additional data load. Additionally, data warehouses can be
flexible to incorporate new data sources and adapt to evolving business needs.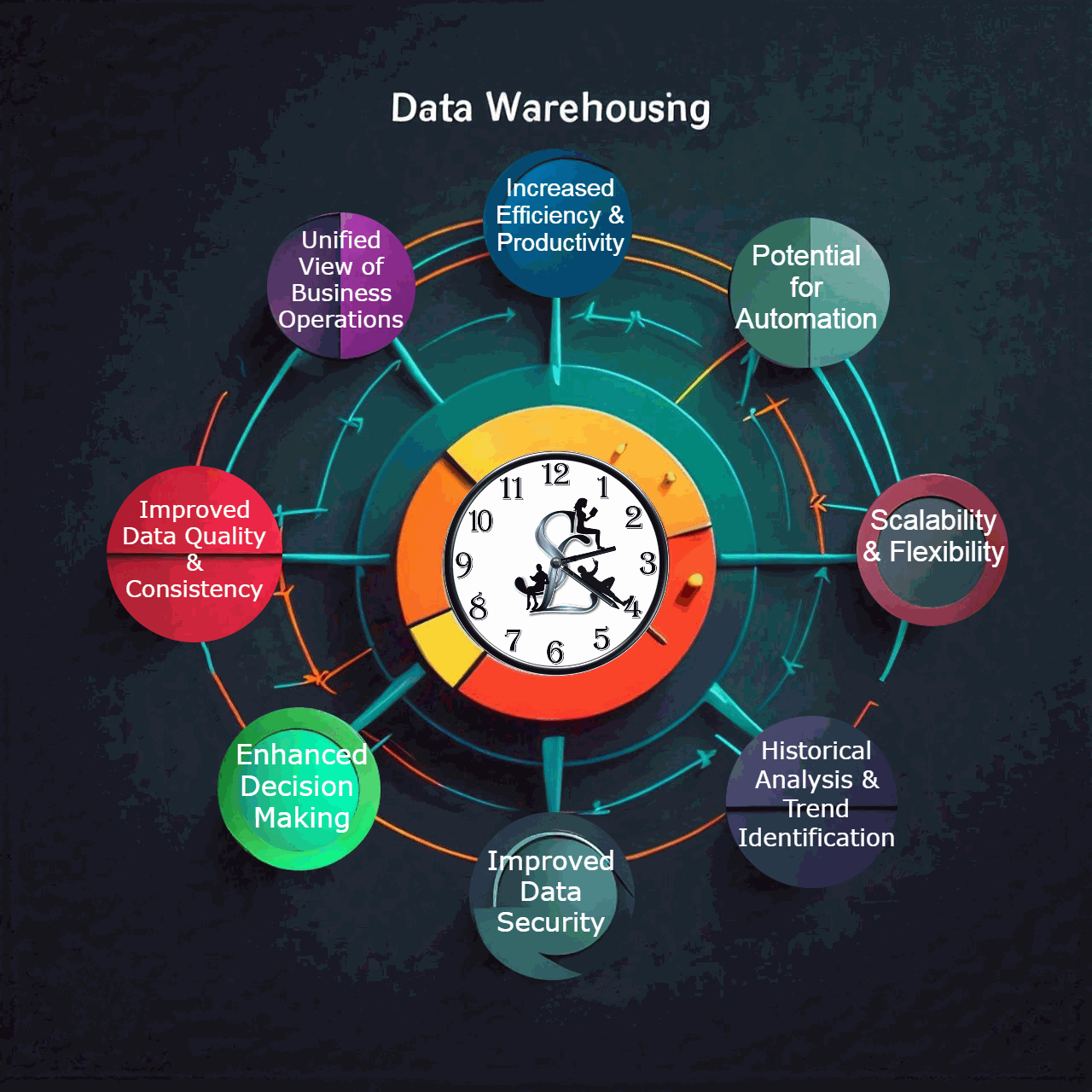
Data Warehousing
A data warehouse is a collection of data that helps managers make decisions. It's organized around important topics like customers, products, and sales, rather than specific tasks like invoicing or stock control. This data comes from different systems and is combined into a single, consistent view. The data is accurate only at a specific point in time or over a certain period, and it's not updated in real-time. Instead, new data is added regularly, building on what's already there.
Think of it like a library:
- Subject-oriented: The library is organized by topics (subjects) like history, science, and fiction.
- Integrated: Books from different authors and publishers are brought together in one place.
- Time-variant: The information in the books is accurate only at the time they were written.
- Non-volatile: New books are added to the library, but they don't replace existing ones. The collection grows over time.
This makes it easier for managers to access and analyze the data they need to make informed decisions.
Benefits of Data Warehousing
Implementing a data warehouse can bring significant benefits to an organization, including:
- High Returns on Investment: Data warehousing can yield an average return on investment of 401% over three years, making it a valuable investment for organizations.
- Competitive Advantage: With access to previously unknown information, organizations can gain a competitive edge in the market.
- Increased Productivity: Data warehousing integrates data from multiple sources, providing a consistent view of the organization and enabling decision-makers to make more informed decisions.
- Cost-Effective Decision-Making: By reducing the number of channels, data warehousing helps organizations make more cost-effective decisions.
- Better Enterprise Intelligence: Data warehousing provides better insights into the organization, enabling more informed decision-making.
- Enhanced Customer Service: By providing a centralized repository of customer data, data warehousing enables organizations to improve customer service.
Problems of Data Warehousing
However, data warehousing also comes with some challenges, including:
- Underestimation of Resources: Data loading can take longer than expected, requiring significant resources.
- Hidden Problems with Source Systems: Undetected problems with source systems can lead to incomplete or inaccurate data.
- Required Data Not Captured: Important data may not be captured by source systems, leading to incomplete analysis.
- Increased End-User Demands: As users become more aware of the data warehouse's capabilities, demands for support and complex queries may increase.
- Data Homogenization: Integrating data from different sources can lead to loss of important data values.
- High Demand for Resources: Data warehousing requires large amounts of data, leading to high resource demands.
- Data Ownership: Data warehousing may lead to reluctance from departments to share sensitive data.
- High Maintenance: Data warehouses require regular maintenance, which can be time-consuming and costly.
- Long-Duration Projects: Building a data warehouse can take up to three years, making it a long-term commitment.
- Complexity of Integration: Integrating different data warehousing tools can be challenging and time-consuming.
